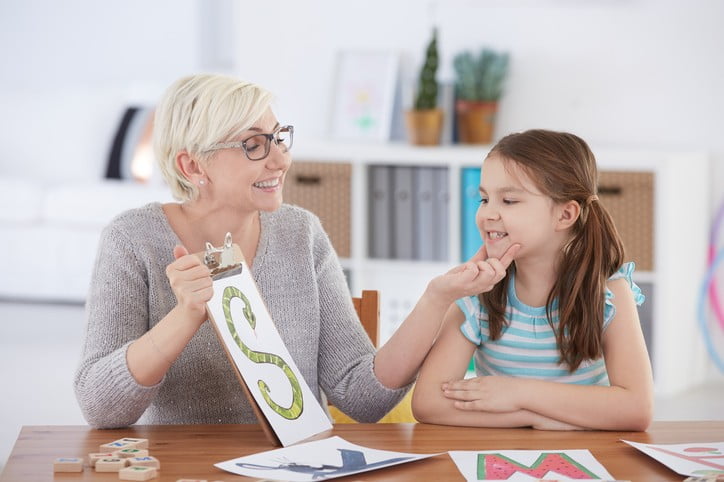
Speech is the process of making fluent sounds that make sense to the listeners. A speech disorder can refer to any condition wherein an individual fails to express feelings by words and sounds. Speech helps people communicate their feelings, sentiments, and thoughts to other people and construct associations. For clear speech, one needs the precise synchronization of various body parts. This article will discuss the types of speech disorders, and the symptoms and therapy of speech disorders are available.
Speech Disorder
Speech problems limit individuals from getting proper speech sounds, while language issues influence an individual’s capacity to understand words or comprehend others’ stories. Notwithstanding, both speech and correspondence problems can make it more difficult for individuals to communicate their sentiments and feelings to other people.
Types of speech problem
Numerous individuals of various ages face speech issues. Some speech problems are faltering, Apraxia, and Dysarthria. We address every one of these kinds beneath:
Faltering
Faltering focuses on a speech problem that forestalls the progression of speech. Individuals who stammer can experience the sorts of disturbance:
Redundancies happen when individuals think that it’s hard to emulate sounds, vowels, or words.
Obstacles happen when individuals don’t talk about what they want to say. In flattering, someone feels like their words are felled. While talking, a person stretches the words or sounds while expressing their viewpoints.
The side effects of stammering can contrast from one individual to another, contingent upon the conditions. Dread, zeal, or dissatisfaction can cause faltering to turn out to be more prominent. A few people only find it challenging to speak specific words or produce sounds which also cause a stammer. Stammering can cause various side effects, including:
Weight in the face and shoulders
Keep squinting
Lip quakes
Held clench hands
Abrupt head developments
There are two fundamental kinds of faltering:
Guardians notice faltering effects in developing youngsters who, as of late, began acquiring speech and language abilities. If an individual has somebody who manages a faltering issue, there may be odds he/she can likewise deal with the same problem. Neurogenic faltering happens when a mind injury stops profound association between the distinctive cerebrum parts of the body that build a speech ability.
Apraxia
The mind is a CPU of the human body. It controls everything that individuals do, including talking. The majority of the mind’s commitment to speech isn’t apparent and programmed. When somebody talks, the mind moves signs to the body’s various designs that work aggregately to deliver a speech. All body parts are associated with each other to frame the fitting sounds.
Apraxia is an overall word alluding to cerebrum ailment that impedes an individual’s scholarly abilities, influencing any piece of the body. Apraxia of speech, or verbal apraxia, applies explicitly to the weakness of engine capacities that affect a person’s capacity to precisely frame speech sounds, in any event, when they realize which words they need to express.
In Dysarthria, the cerebrum debilitates the bones of an individual’s face, lips, tongue, throat, or chest. If your face muscles are weak, then it can cause a problem in fluent speaking. Individuals who have Dysarthria may experience the accompanying indications:
Distorted Speech
Muttering
Talking too purposely or excessively fast
Delicate or calm speech
Trouble moving the jaws or tongue
Our speech therapist Adelaide has certified for both adults and childrens . Get in touch with us for any assistance